Friday, 18 July, 2025
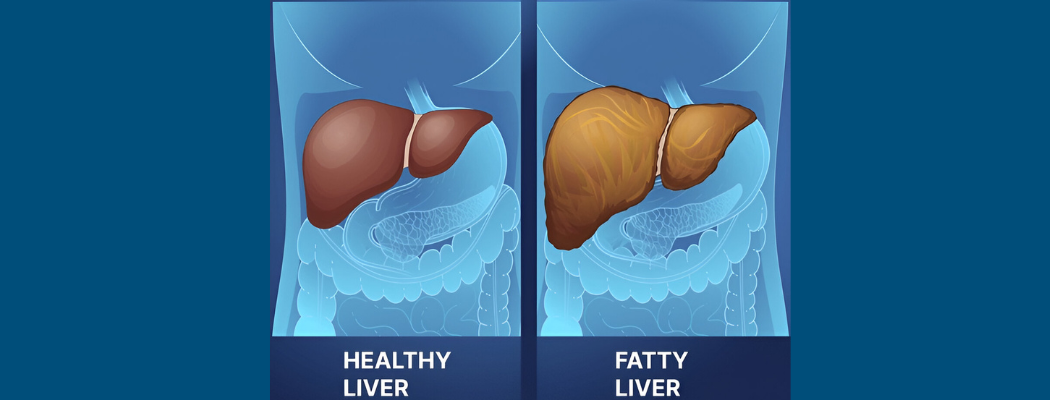
What is fatty liver disease? It is a common condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. It is often linked to lifestyle factors such as diet, obesity, and alcohol consumption. In many cases, fatty liver disease is asymptomatic in its early stages but can progress to severe liver complications if left untreated. This article delves into its types, causes, fatty liver disease symptoms, and how to reduce fatty liver quickly to help you understand how to protect your liver health.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
The liver is a crucial organ responsible for detoxification, metabolism, and digestion. When fat makes up more than 5-10% of the liver's weight, it is classified as fatty liver disease. While a small amount of liver fat is normal, excess fat can lead to inflammation, liver damage, and even scarring (cirrhosis) over time.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease can be categorized into two main types:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
What is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? NAFLD is the most common form of fatty liver disease, affecting individuals who consume little to no alcohol. It is closely associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol. NAFLD can further progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form that involves liver inflammation and fibrosis, potentially leading to cirrhosis or liver failure.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
AFLD results from excessive alcohol consumption, which disrupts liver function and leads to fat accumulation. Over time, fatty liver disease due to alcohol can progress to alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis, significantly impairing liver function. Reducing alcohol intake is crucial in preventing the worsening of this condition.
Fatty Liver Disease Causes and Risk Factors
Genetics and Family History
Genetics play a role in the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. If a close family member has a history of liver disease, you may have a higher risk of developing NAFLD.
Unhealthy Diet and Obesity
A diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and added sugars can lead to fat accumulation in the liver. Obesity, particularly abdominal obesity, is a significant fatty liver disease cause.
Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
Fatty liver disease diabetes management is essential because people with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance have a higher chance of developing fatty liver disease. Insulin resistance increases fat storage in the liver, leading to inflammation and damage over time.
High Cholesterol and Metabolic Syndrome
Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides contribute to fat buildup in the liver. Metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels, increases the risk of NAFLD.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol is a major toxin that the liver must process. Heavy drinking can overwhelm the liver, leading to fat accumulation, inflammation, and scarring. Reducing alcohol intake is key to preventing AFLD.
Symptoms and Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is often called a "silent" disease because it typically has no symptoms in its early stages. However, some individuals may experience:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Mild abdominal discomfort
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Dark urine and pale stool
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- A general feeling of discomfort or bloating after meals
Fatty Liver Symptoms in Males and Females
Fatty liver symptoms in males and females can vary slightly. Males may experience a higher tendency for inflammation, while females might develop liver-related hormonal imbalances. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal bloating and pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swollen legs and feet (due to fluid retention)
- Mental confusion (in severe cases of liver dysfunction)
- Hormonal imbalances that may cause menstrual irregularities in females
- Decreased testosterone levels and fatigue in males
If you suspect any of these symptoms, visit & consult a liver hospital in Bangalore for expert medical care.
Stages of Fatty Liver Disease Progression
So the question most of them have is how many stages of fatty liver disease are there?
- Grade 1 Fatty Liver Disease (Steatosis): Excess fat accumulates in the liver but does not cause significant inflammation or damage.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) or Alcoholic Hepatitis: Inflammation occurs, leading to liver damage.
- Fibrosis: Persistent inflammation causes scarring of liver tissue.
- Cirrhosis: Extensive scarring leads to liver failure, increasing the risk of liver cancer.
How to Manage and Treat Fatty Liver Disease?
Dietary Modifications for a Healthier Liver
What is the best diet for fatty liver disease? A healthy diet plays a key role in managing and reversing fatty liver disease. Some dietary recommendations include:
- Consuming a balanced fatty liver disease diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Reducing sugar and refined carbohydrates to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Including healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids from fish and nuts.
- Avoiding processed foods, fried foods, and excessive salt intake.
- Staying hydrated with plenty of water and herbal teas.
- Incorporating liver-friendly foods such as turmeric, garlic, and green leafy vegetables.
Exercise and Physical Activity
How to reduce fatty liver quickly? Regular exercise helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improves overall metabolic health. Recommended activities include:
- Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, or cycling for at least 30 minutes daily.
- Strength training to improve muscle mass and metabolic function.
- Yoga and stretching exercises to promote relaxation and liver health.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) for improving insulin sensitivity and fat metabolism.
- Core strengthening workouts to improve digestion and metabolic rate.
Medical Treatments and Medications
Fatty liver disease treatments include managing underlying conditions and avoiding harmful substances. Medications to avoid with fatty liver disease include certain painkillers, steroids, and cholesterol medications that may stress the liver.
While there is no specific FDA-approved medication for NAFLD, certain treatments may help manage underlying conditions:
- Medications for diabetes to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs to reduce liver fat.
- Vitamin E supplements may be beneficial for some NAFLD patients.
- Liver transplant in severe cases of cirrhosis.
- Antioxidant therapy to reduce oxidative stress on liver cells.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
Many natural remedies and supplements may help improve liver function and reduce fat accumulation. These include:
Milk Thistle
Known for its liver-protective properties, milk thistle contains silymarin, which helps reduce liver inflammation and oxidative stress.
Turmeric (Curcumin)
A powerful anti-inflammatory compound that may help reduce liver fat buildup and improve liver function.
Green Tea Extract
Contains antioxidants called catechins that promote fat metabolism and support liver health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Found in fish like salmon and flaxseeds, omega-3s help reduce liver fat and inflammation.
Probiotics
Probiotic foods for gut health are closely linked to liver function. A healthy gut microbiome can help reduce liver fat.
Dandelion Root
Traditionally used for liver detoxification, dandelion root may support bile production and improve digestion.
Garlic
Helps reduce liver fat accumulation and supports overall metabolic health.
Caffeine (Coffee)
Studies suggest that moderate coffee consumption may help reduce liver fat and inflammation.
Also Read: 12 Science-Backed Benefits of Black Coffee You Should Know
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Many of them wonder how to prevent fatty liver? The below are few lifestyle changes that helps in prevention of fatty liver:
- Limiting alcohol intake to prevent AFLD.
- Managing weight through a healthy diet and exercise.
- Controlling diabetes and cholesterol levels to reduce liver stress.
- Regular health check-ups to monitor liver function and detect early symptoms of fatty liver disease.
- Avoiding exposure to toxins that may affect liver health.
- Maintaining stress levels through meditation and adequate sleep.
Conclusion
Is fatty liver dangerous? If left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure. However, it is largely preventable and manageable through healthy lifestyle choices. By maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing underlying health conditions, individuals can reduce their risk and even reverse early-stage fatty liver disease.
Early diagnosis and proactive management are key to maintaining liver health and preventing complications. If you suspect fatty liver disease, consult a fatty liver disease specialist in Bangalore for proper assessment and guidance on the best treatment approach.
FAQ’s
-
How long does it take to reverse fatty liver?
The time required to reverse fatty liver depends on lifestyle changes, diet, and exercise. With consistent healthy habits, mild fatty liver disease can improve within 3 to 6 months, while more severe cases may take a year or longer to show significant improvement. Life expectancy with fatty liver disease improves significantly when managed early. -
Is fatty liver disease linked to other health conditions?
Yes, fatty liver disease is closely linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. It can also increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and liver-related complications. Additionally, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease symptoms are often associated with other metabolic disorders. -
Can children develop fatty liver disease?
Yes, pediatric NAFLD is becoming more common due to rising childhood obesity and unhealthy diets. It can lead to long-term liver damage if not managed early with proper nutrition and physical activity. -
What are the long-term risks of untreated fatty liver disease?
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. It also increases the risk of liver cancer and cardiovascular diseases.


 Neurosciences
Neurosciences Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric Surgery